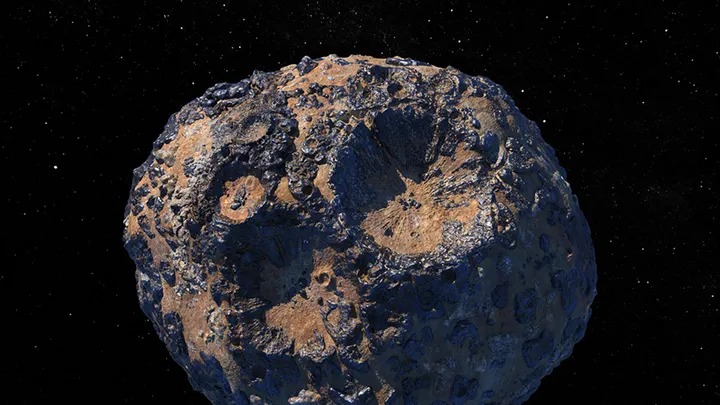
The probe is scheduled to launch from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s launch pad 39A in Florida at 10.38 a.m. EDT on October 5. Washington, Sep 7 (IANS) NASA’s Psyche project, which aims to examine a metal-rich asteroid. The Psyche mission is a voyage to the same-named metal-rich asteroid that orbits the Sun between Mars and Jupiter.
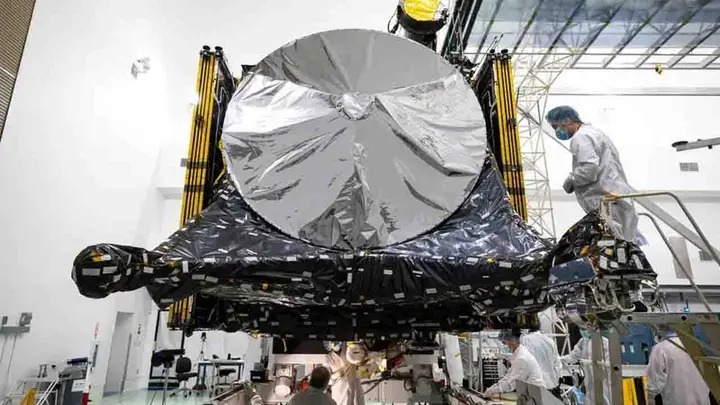

The NASA probe expedition Psyche could help scientists learn more about the formation of planets
All four thrusters completed their final tests. Engineers confirmed that the huge high-gain antenna is now transmitting data. “These missions take so many people and so much careful, rigorous, personally driven work,” said Lindy Elkins-Tanton, chief investigator for Psyche at Arizona State University, in a release.
“I’m prepared to be ecstatic. We are all happy, but not overjoyed. Technicians will begin wrapping the spacecraft in its payload fairing (the cone at the top of the rocket) within two weeks.
- Advertisement -
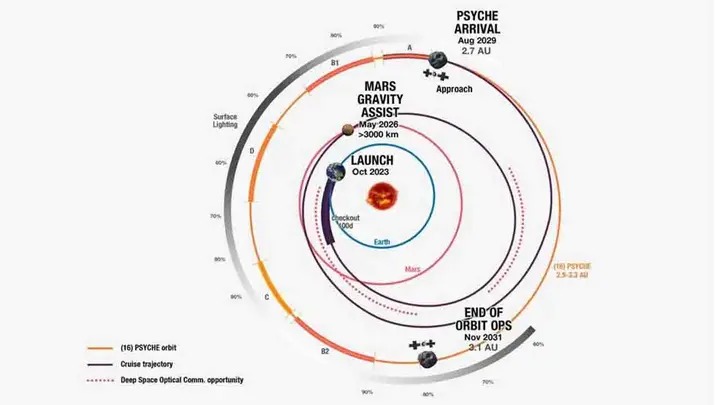
Psyche will offer an opportunity to investigate a metal-rich asteroid for studies
Psyche will use solar electric propulsion to complete its six-year voyage to the asteroid after escaping Earth’s gravity. The efficient propulsion system works by accelerating and releasing charged atoms, or ions, of the neutral gas xenon. Creating a thrust that softly drives the spacecraft with the force of a single AA battery in your hand.
The asteroid Psyche offers a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity to investigate a metal-rich material. That could be part of a planetesimal core, the building component of an early planet. Once the spacecraft reaches the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, it will orbit the asteroid for about 26 months. It will then start acquiring images and other data that will help scientists learn more about its history and composition.
The mission was postponed by a week so that NASA could finish verifications of the parameters required to control the spacecraft’s gas thrusters. This includes modifying them for warmer temperature projections.



