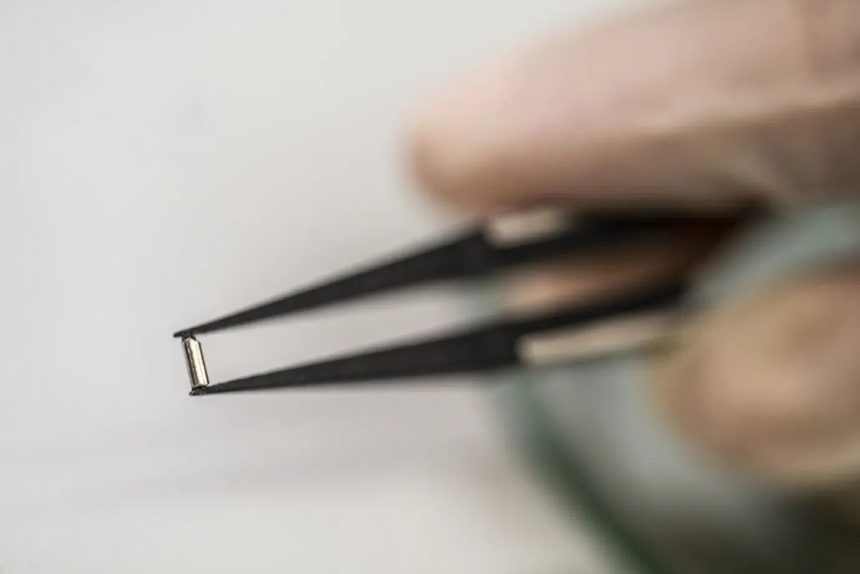
Smaller than a grain of rice implantable device has been demonstrated to reduce pancreatic cancers. One of the most aggressive and difficult-to-treat tumors is pancreatic cancer. By using a device that is smaller than a grain of rice to administer immunotherapy straight into the tumor, Houston Methodist nano medicine specialists have found a way to manage it.
According to accounts, researchers at the Houston Methodist Research Institute used an inserted nanofluidic device they developed to administer CD40 monoclonal antibodies (mAb). In murine models, tumors were decreased at a dosage four times lower than with standard systemic immunotherapy.

This shows that the immune system was successfully stimulated by local immunotherapy to attack other tumors. One animal model didn’t develop a tumor over the next 100 days of observation. Usually, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is detected in advanced stages. Around 85 percent of patients already have metastatic disease when they receive a diagnosis.
- Advertisement -
Immunotherapy: Side Effects of Pancreatic Device
Cancers for which there have never been effective medicines before may be treated with immunotherapy. However, immunotherapy usually causes long-lasting negative effects because it is given all over the body. The body is protected from dangerous drugs by concentrating its supply on the tumor. Having fewer side effects, therefore raising the standard of living for those getting treatment.
The Grattoni Nanomedicine Lab at Houston Methodist is a specialist in implantable nanofluidics-based technologies for long-term, controlled medication delivery and cell transplantation for the treatment of chronic disorders.
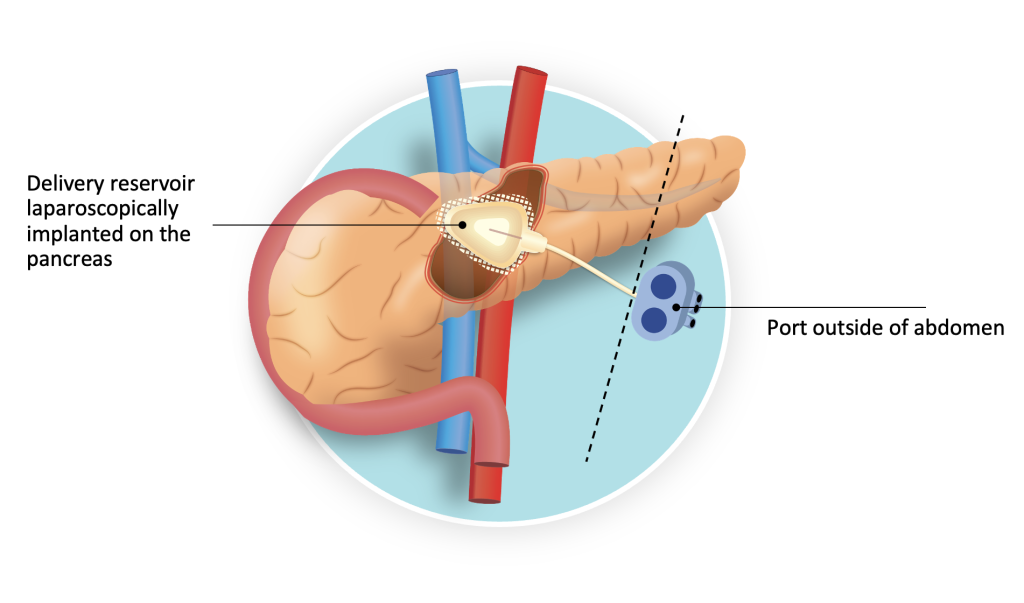
A stainless steel medication reservoir with nanochannels makes up the NDES device. Make a membrane that allows prolonged diffusion once the medication is released.
The
Smaller than a grain of rice implantable device has been demonstrated to reduce pancreatic cancers. One of the most aggressive and difficult-to-treat tumors is pancreatic cancer. By using a device that is smaller than a grain of rice to administer immunotherapy straight into the tumor, Houston Methodist nano medicine specialists have found a way to manage it.
According to accounts, researchers at the Houston Methodist Research Institute used an inserted nanofluidic device they developed to administer CD40 monoclonal antibodies (mAb). In murine models, tumors were decreased at a dosage four times lower than with standard systemic immunotherapy.
This shows that the immune system was successfully stimulated by local immunotherapy to attack other tumors. One animal model didn’t develop a tumor over the next 100 days of observation. Usually, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is detected in advanced stages. Around 85 percent of patients already have metastatic disease when they receive a diagnosis.
Immunotherapy: Side Effects of Pancreatic Device
Cancers for which there have never been effective medicines before may be treated with immunotherapy. However, immunotherapy usually causes long-lasting negative effects because it is given all over the body. The body is protected from dangerous drugs by concentrating its supply on the tumor. Having fewer side effects, therefore raising the standard of living for those getting treatment.
The Grattoni Nanomedicine Lab at Houston Methodist is a specialist in implantable nanofluidics-based technologies for long-term, controlled medication delivery and cell transplantation for the treatment of chronic disorders.
A stainless steel medication reservoir with nanochannels makes up the NDES device. Make a membrane that allows prolonged diffusion once the medication is released.
The Houston Methodist nanofluidic device is intended for long-term controlled and sustained release to avoid repeated systemic treatment, which often results in negative side effects.



